BayMeters
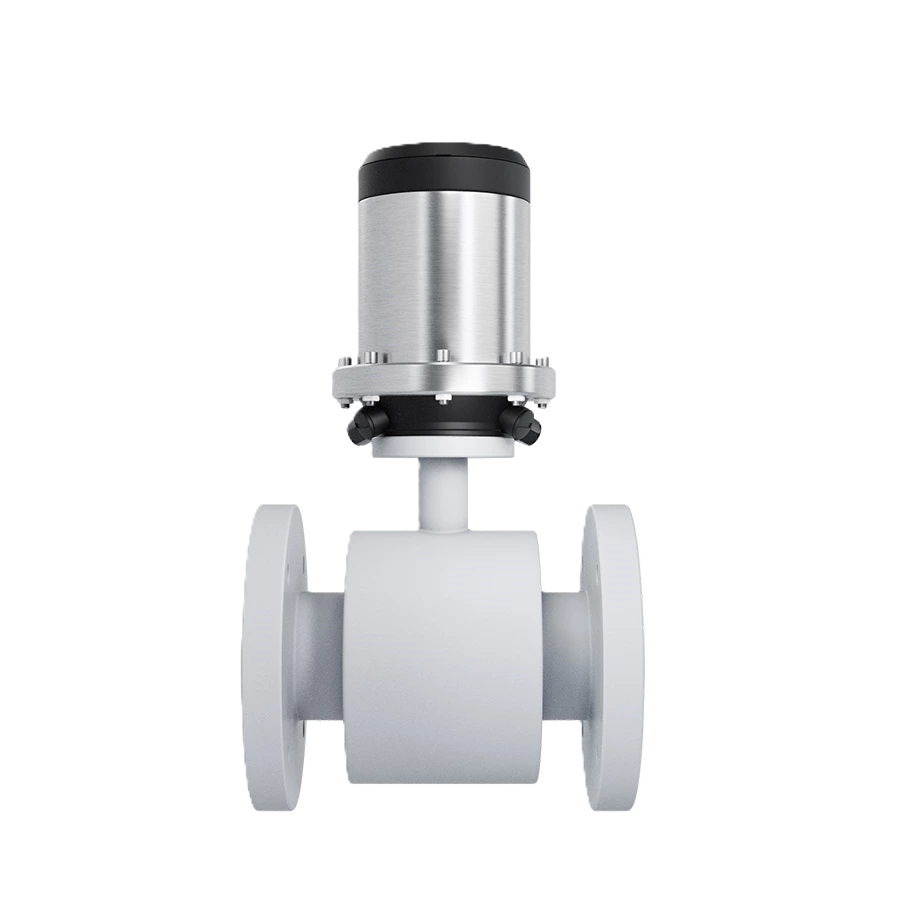
Battery powered magnetic flowmeter LDG
Battery powered magnetic flowmeter LDG
Share

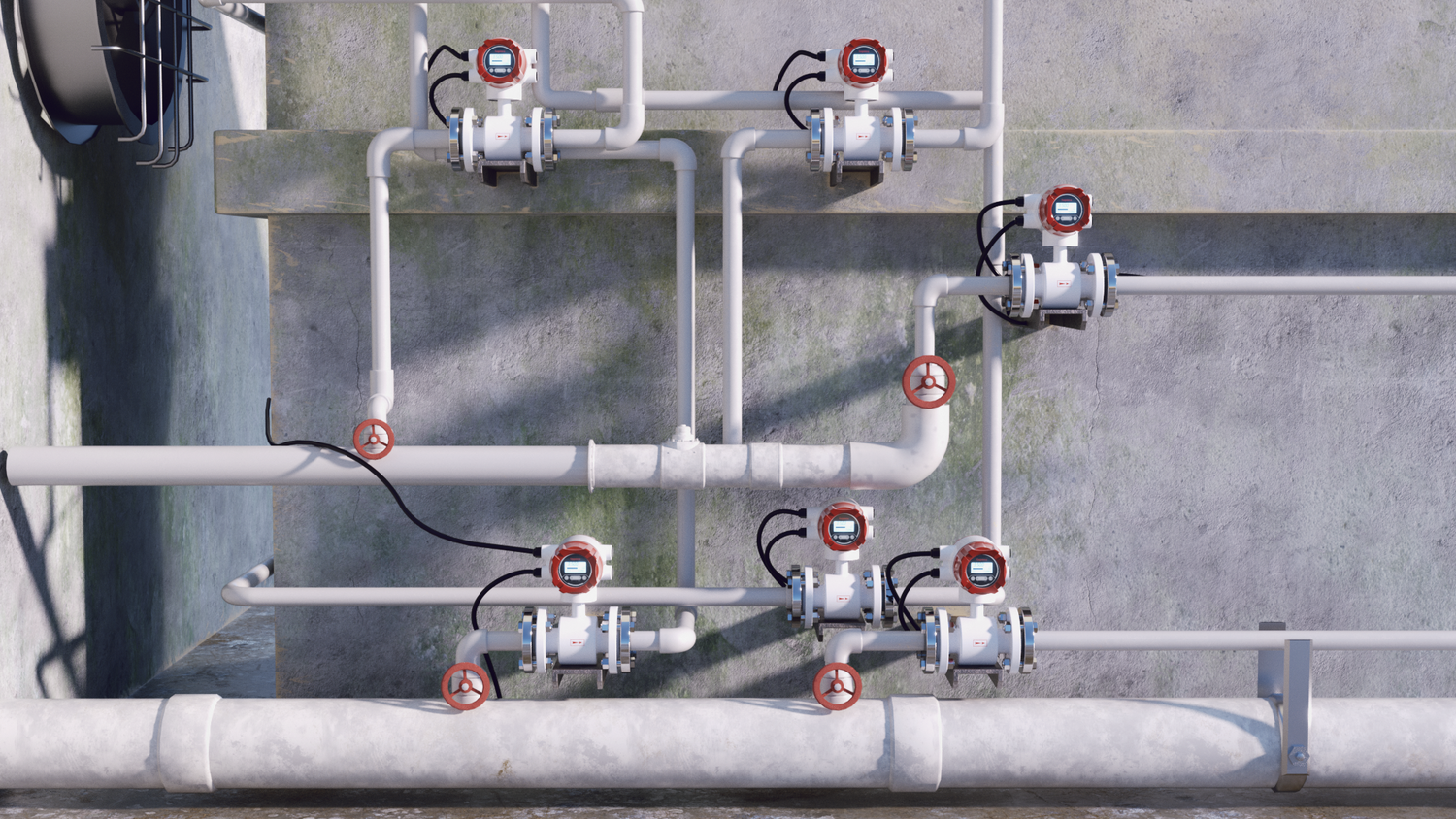
Introduction
The battery-powered electromagnetic flow meter converter adopts internal battery power supply without external power supply. It is suitable for working conditions where the field power grid cannot be reached and the power grid is difficult to lay. It is especially suitable for the monitoring, metering and settlement of the tap water supply system.
Specification
Diameter Nominal
DN15(1/2”)~DN1200(48”)
Accuracy
0.5%
Environmental Temperature
-20℃~50℃ (-4℉~122℉)
Relative Humidity
≦95%
Lining Material
PTFE, PFA, F46, neoprene, polyurethane rubber, high temperature rubber
Flow Range
0-15 m/s (0-49.21 ft/s)
Conductivity
Clean water >20 μs/cm
Communication
RS485 (Modbus protocol), GPRS
Electrode Material
SS316, Hastelloy B/C, titanium, tantalum, platinum-iridium alloy, tungsten carbide
Electrode Type
Standard, scraper, replaceable
Connection
Flange, plug-in, clamp, clip-on
Medium Temperature
-20℃~+60℃ (-4℉~140℉)
Nominal Pressure
0.6~4.0 MPa (87~580 psi, other can be customized)
Measurement Parameter
Instantaneous flow, instantaneous flow rate
Record Parameter
Accumulated total flow
Detection and Alarm Parameters
Fluid empty pipe detection alarm, excitation current detection alarm
Test Mode Output Signal
Unit volume flow pulse
Details
Multiple work mode
LCD display with multiple Flow Units Selectable 'Flow Only' 'Flow+Pressure' 'Flow+ Temperature'
Intelligent converter
Digital Signal Processing, Stable measurement, High Accuracy, Strong Anti-interference Capability
Technology upgrade
The material of the lining isanti-falling, anti separtion, anti-leakage, and prolongs the service life
Micro-power consumption
Battery life 5-8 years, easy to replace battery
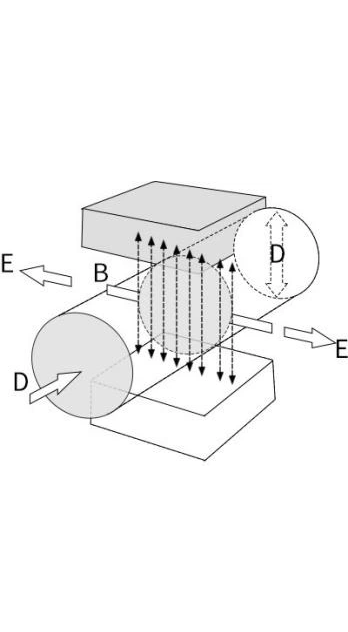
Measuring principle
Mag meter works based on Faraday's law, when the liquid goes through the pipe at the flow rate of v with a diameter D, within which a magnetic flux density of B is created by an exciting coil, the following electromotive E is generated in proportion to flow speed v:
E=K×B×V×D
Where:
E-Induced electromotive force
K-Meter constant
B-Magnetic induction density
V-Average flow speed in cross-section of measuring tube
D-Inner diameter of measuring tube
Application


